What Is The Difference Between Halogen and LED Light Bulbs: Essential Guide
Choosing the right type of light bulb for your home or office can significantly impact energy efficiency, comfort, and even your wallet. Two of the most popular options, halogen and LED light bulbs, offer different benefits and drawbacks.
Halogen bulbs operate by using a halogen gas to increase the life span and light output of traditional incandescent bulbs. In contrast, LED (Light Emitting Diode) bulbs utilise semiconductor technology, converting electric current directly into visible light. As a result, LED bulbs are more energy efficient and have a longer life span compared to halogen bulbs.
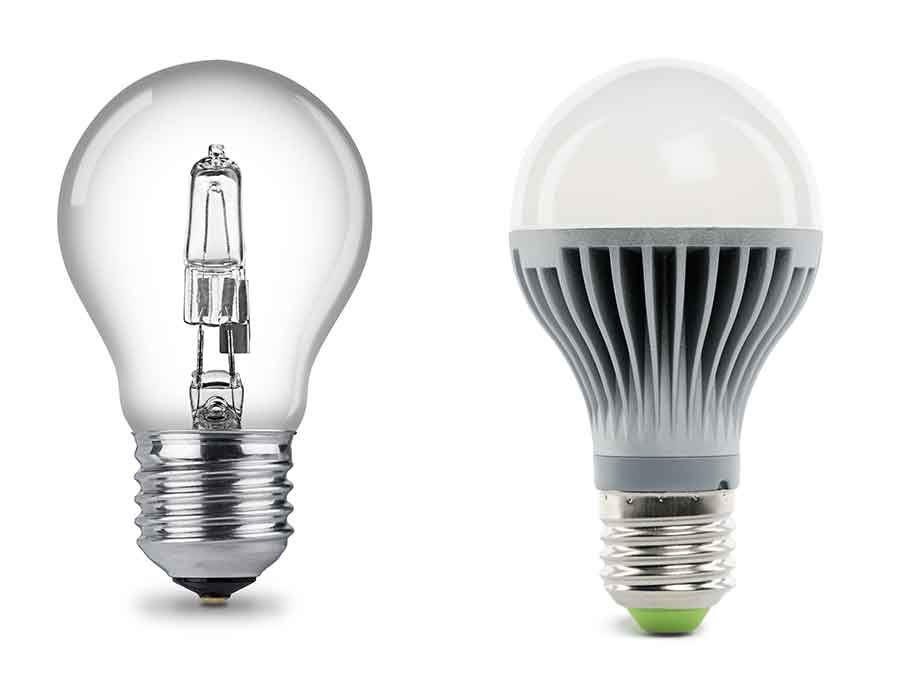

Understanding the difference between halogen and LED light bulbs will help you make an informed decision when selecting the best lighting solution for your needs. This article will explore the key differences between these two types of bulbs and provide insights into their efficiency, lifespan, and cost, among other factors.
Understanding Halogen Bulbs
Halogen bulbs are a type of incandescent light bulb that use halogen gas to emit light. They have been in use for many years and can be found in various lighting applications. In this section, we will explore the working principle of halogen bulbs, as well as their pros and cons.
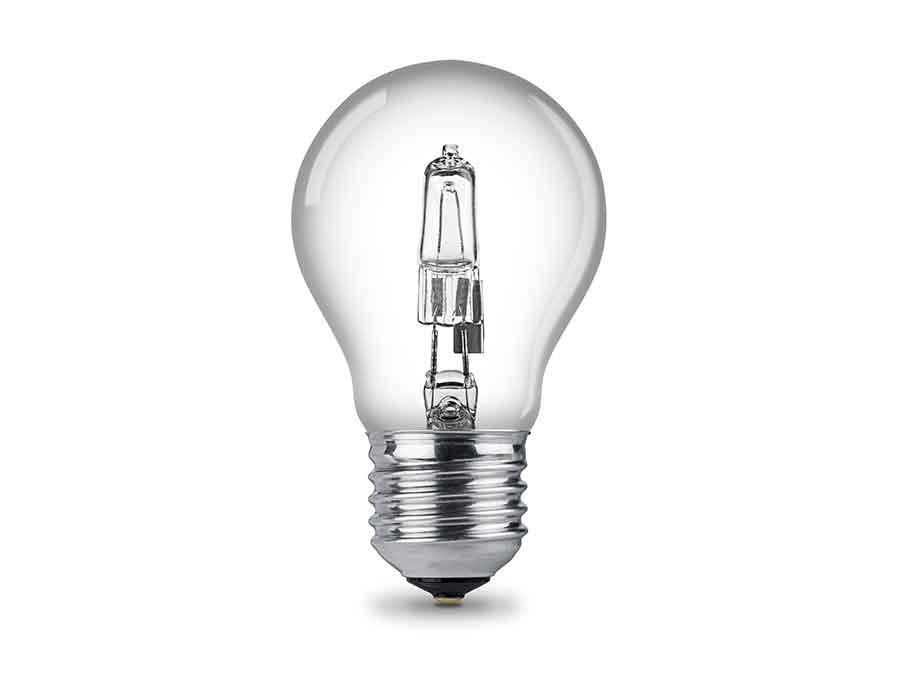

Working Principle
Halogen bulbs consist of a tungsten filament enclosed in a small quartz or hard glass envelope filled with halogen gas. When electric current passes through the filament, it heats up and emits visible light. The halogen gas helps to extend the life of the filament by creating a chemical reaction that continuously redeposits evaporated tungsten back onto the filament, known as the halogen cycle.
Pros and Cons
There are several advantages and disadvantages to using halogen bulbs, which will be discussed below.
- Pros:
- Lower initial cost: Halogen bulbs are usually cheaper to purchase than their LED counterparts.
- Wide colour temperature range: They can produce a warm or cool light, making them suitable for various settings.
- Dimmable: Unlike some LED bulbs, halogen bulbs are easily dimmable, which allows for greater control over lighting levels in a room.
- Cons:
- Energy inefficiency: Halogen bulbs are less energy-efficient than LEDs and consume more power to produce the same amount of light.
- Shorter lifespan: They have a shorter lifespan compared to LED bulbs, which means they need to be replaced more frequently.
- Heat output: Halogen bulbs can produce a significant amount of heat, which can be a safety concern and might affect the temperature in a room.
In the next sections, we will discuss LED light bulbs and compare their features with halogen bulbs to help you make an informed decision when choosing a lighting solution.
Understanding LED Bulbs
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode, a semiconductor device that converts electrical energy into light. In this section, we will review the working principle of LED bulbs and their pros and cons.

Working Principle
When a current passes through the diode, a semiconductor material within the structure allows electrons to combine with holes, releasing energy in the form of photons (light). This process is called electroluminescence.
Pros and Cons
There are several advantages and some disadvantages to using LED bulbs.
| Pros | Cons |
| Energy efficient: LEDs consume up to 90% less electricity than traditional bulbs.Long-lasting: Life spans of 25,000-50,000 hours are common, reducing replacement costs.Eco-friendly: LEDs do not contain harmful substances like mercury, common in CFLs.Various colours and applications: LEDs can emit a wide range of colours for versatile uses. | Higher initial cost: LEDs can be more expensive upfront, but typically pay off in the long run.Sensitivity to high temperatures: Extreme heat can affect the performance of LED bulbs.Directional light: LED bulbs emit light in specific directions, which may not be ideal for all spaces. |
Performance Comparison
In order to understand the differences between halogen and LED light bulbs, this section will break down the key aspects of each technology, discussing their energy efficiency, lifespan, and brightness.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a crucial metric when comparing light bulbs, as it directly affects electricity consumption and costs.
- Halogen: These bulbs are less energy-efficient, as they convert a larger proportion of energy into heat rather than light.
- LED: In contrast, LED bulbs are much more energy-efficient, as they convert most energy into light with minimal heat output. They also consume less power to produce the same amount of light compared to halogen bulbs.
Lifespan
The lifespan of a light bulb is another important factor to consider when making comparisons.
- Halogen: These bulbs typically have a shorter lifespan of around 2,000 to 4,000 hours.
- LED: LED bulbs, on the other hand, can last significantly longer, with some options boasting up to 25,000 to 50,000 hours of use.
Brightness
Brightness is measured in lumens, and it is essential to consider how much light a bulb can produce when comparing halogen and LED options.
- Halogen: Halogen bulbs can produce high levels of brightness, with instant response times when turned on. However, they can lose brightness over time.
- LED: LEDs produce consistent brightness throughout their lifespan, which does not degrade over time. They also offer greater control over colour temperature and come in a wide range of options to suit various needs.
Environmental Impact
When comparing halogen and LED light bulbs, their environmental impact differs significantly. Both bulbs have unique features that can influence energy use, waste production, and recyclability.
Energy Consumption:
- Halogen: Halogen bulbs typically consume more energy than LEDs, often lasting for only 1,000 to 3,000 hours. Their shorter lifespan can lead to frequent replacements, contributing to increased energy consumption and waste.
- LED: LEDs are known for their energy efficiency, using 85% to 90% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs. They also boast an impressive lifespan of 15,000 to 50,000 hours, reducing the need for frequent replacements, and resulting in lower energy consumption and waste.
Recyclability and Waste:
- Halogen: Disposing of halogen bulbs can prove complicated, as breaking a bulb can release harmful chemicals. This makes it essential to recycle them responsibly, though recycling facilities may not always be readily available in certain areas.
- LED: LEDs are more environmentally-friendly waste-wise, as they don’t contain harmful chemicals and are easier to recycle. Many recycling centres are also equipped to handle LEDs, further contributing to their low environmental impact.
Potential Heat Emission:
- Halogen: Most of the energy consumed by halogen bulbs is lost as heat, releasing not only unnecessary heat but also increasing the need for energy to cool the space. This affects the efficiency of these lights and can inadvertently place greater pressure on the environment.
- LED: LEDs emit very little heat, as their energy consumption primarily goes towards producing light. As a result, LEDs contribute to a more comfortable environment while using energy more efficiently, making them a preferable choice for those seeking to minimise their environmental impact.
Comparison of LED vs Halogen Power Consumption
The power consumption of light bulbs is usually measured in watts, which indicates the energy consumption rate. When comparing LED and halogen light bulbs, it is essential to evaluate their power consumption, as this is linked to energy efficiency and cost savings.
LED bulbs require significantly less energy than halogen bulbs. Generally, an LED bulb requires roughly:
- 5-10 watts for a standard 60-watt halogen replacement
- 8-12 watts for a 75-watt halogen replacement
- 16-20 watts for a 100-watt halogen replacement
On the other hand, halogen bulbs consume more energy, with a typical wattage range of 40-100 watts. This higher energy consumption translates to higher costs and increased carbon emissions. The table below compares the power consumption of LED and halogen bulbs when used for 25,000 hours:
| Bulb Type | Wattage | Energy Consumption (kWh) |
| LED | 10W | 250 kWh |
| Halogen | 60W | 1,500 kWh |
The table illustrates that using LED bulbs instead of halogen bulbs can result in substantial energy savings. Furthermore, lower energy consumption not only reduces electricity bills but also contributes to a greener environment by decreasing carbon emissions.
Cost and ROI Analysis
When comparing halogen and LED light bulbs, it’s essential to consider cost and return on investment (ROI). In this section, we will analyse the upfront cost, energy consumption, and the average lifespan of both types of bulbs.
Upfront Cost:
- Halogen bulbs: Generally cheaper than LED bulbs.
- LED bulbs: More expensive initially but have a longer lifespan, which can reduce long-term costs.
Energy Consumption:
- Halogen bulbs: Consume more energy than LED bulbs, leading to higher energy bills.
- LED bulbs: Significantly more energy-efficient, which can result in significant energy savings.
Average Lifespan:
- Halogen bulbs: Typically last for 2,000 to 4,000 hours.
- LED bulbs: Can last up to 25,000 to 50,000 hours, which is notably longer than halogen bulbs.
When calculating ROI, it is crucial to consider the reduced energy consumption and longer lifespan of LED bulbs. Although the initial investment may be higher for LED bulbs, the potential long-term savings could outweigh the upfront cost difference.
Compatibility and Installation
When considering the switch from halogen to LED light bulbs, it’s important to understand their compatibility and ease of installation. The compatibility of LED bulbs depends on the type of light fixture and the dimmer switches in use.
LED bulbs are generally designed to be backward compatible with traditional fixtures, meaning they fit into the same socket with few modifications. There are different types and sizes of LED bulbs to accommodate the various lighting fixtures available. Some common types include:
- GU10 LEDs – for spotlights and downlights
- E27 or B22 LEDs – for standard screw or bayonet lamps
- MR16 or G4 LEDs – for smaller spotlights and fitting types
Dimmer switches can sometimes pose an issue in compatibility. If your current dimmer switch is old, it may not be compatible with LED bulbs, which may result in flickering or reduced dimming capabilities. To solve this issue, you may need to replace the dimmer switch with one specifically made for LED bulbs.
When it comes to installation, most LED bulbs can be easily installed by following a few simple steps:
- Switch off the power supply to ensure safety.
- Remove the old halogen bulb from the fixture. It is important to let it cool down before handling, as halogen bulbs can become extremely hot.
- Insert the new LED bulb into the fixture, ensuring it fits securely and is aligned correctly.
- Restore power to the fixture and test the LED bulb to ensure it is functioning properly.
While upgrading to LED bulbs is generally straightforward, it is a good idea to consult a professional for more complex installations or if you encounter any issues during the process.
Conclusion
In summary, the key differences between halogen and LED light bulbs are their energy efficiency, lifespan, heat emission, and cost. LED bulbs are significantly more energy-efficient and eco-friendly, with a longer lifespan compared to halogen bulbs. They also emit less heat and are often considered safer for prolonged use.
However, halogen bulbs are typically cheaper upfront, which may appeal to some consumers on a tight budget. When considering long-term costs and the environmental impact, LED bulbs prove to be the better investment.
It’s important for consumers to weigh their options and choose the most suitable bulb for their specific needs, keeping in mind factors such as brightness, colour temperature, and compatibility with dimmer switches. By understanding the differences between halogen and LED bulbs, one can make an informed decision about the best lighting solution for their home or business.