What Kind of Electrical Wire Can Be Buried Underground?
When considering electrical installations for outdoor or underground use, it’s essential to know what type of electrical wire can be buried underground. There are various types of cables designed specifically for direct burial, ensuring the safety and longevity of your electrical connections. These cables not only offer protection against moisture but also provide a solid thermoplastic sheath encasing the conducting wires inside.
Some common types of direct burial cables include USE/USE-2, UF-B, Copper Tracer, and Aluminum URD. Each cable serves its unique purpose and offers specific advantages depending on the application. The UK has regulatory standards for burying electrical wires, ensuring that the correct type of cable is utilized, and the appropriate installation procedures are followed.
Key Takeaways
- It’s essential to select the appropriate direct burial cables for underground electrical installations
- Common direct burial cables include USE/USE-2, UF-B, Copper Tracer, and Aluminum URD
- UK regulatory standards ensure proper handling and installation of underground electrical wires.
Types of Electrical Wires That Can Be Buried Underground
UF-B Wires
UF-B wires, or Underground Feeder-B, are suitable for direct burial underground. They consist of multiple conductors surrounded by a moisture-resistant and flame-retardant PVC outer layer. This type of wire is commonly used in residential and commercial applications, as it provides a reliable and safe connection for electrical systems in your garden, shed, or detached garage. The PVC outer layer ensures excellent protection against moisture and soil contact, making UF-B wires a reliable choice for burying underground.
THHN/THWN Wires
THHN and THWN wires are another suitable type of electrical wire for burying underground, but they should be encased in a conduit. THHN (thermoplastic high heat-resistant nylon) and THWN (thermoplastic heat- and water-resistant nylon) wires are coated with a protective PVC insulation layer and a nylon outer jacket, which provides excellent resistance to oil, gas, and abrasion. However, since the nylon outer coating is not designed for direct contact with soil or moisture, it’s essential to use a conduit to protect these wires when burying them underground.
Low Voltage Landscape Wires
Low voltage landscape wires are designed specifically for outdoor lighting, irrigation control systems, and other low-voltage applications. These wires are safe for direct burial and come in various sizes and gauges, depending on your power requirements. Low voltage landscape cables usually comprise a combination of copper conductors and a durable insulation material, like PVC or XLPE, which effectively protects them against environmental factors. When choosing low voltage landscape wires for your project, always ensure they’re rated for direct burial and follow each specific application’s guidelines.

Important Factors to Consider
When selecting the appropriate electrical wire to bury underground, there are several factors you need to consider.
First, the chosen wire must be rated for direct burial. Direct-burial cables are specifically designed for outdoor use and can be buried underground with or without a conduit. For instance, aluminium URD (Underground Residential Distribution) cables meet the regulations for direct-burial applications, according to the National Electrical Code (NEC) – NEC 300.5.
Secondly, you must adhere to the correct depth requirements when burying cables. In the UK, regulations state that cables should be buried at least 18 inches (approximately 45 cm) below the ground’s surface. Deeper burial may be required in specific cases or areas for increased safety.
Moreover, the type of cable should be considered according to the environment it will be installed in. In some cases, steel wire armoured (SWA) cables or pyrotenex cables are required. In other situations, you may use other cables, such as twin and earth, as long as they are placed in a conduit and have adequate moisture protection.
Furthermore, when cables are buried in a concrete floor, the SWA cables or conduits should be protected by a minimum of 1 inch (about 2.5 cm) of concrete, ensuring additional safety and durability.
Finally, ensure you follow safe working practices when installing underground cables. Planning, use of plans, cable locating devices, and safe digging practices should all be employed to minimise risks associated with damaging underground cables. Remember that damage to underground electrical cables can result in fatal or severe injuries, so it is essential to take precautions to avoid danger.
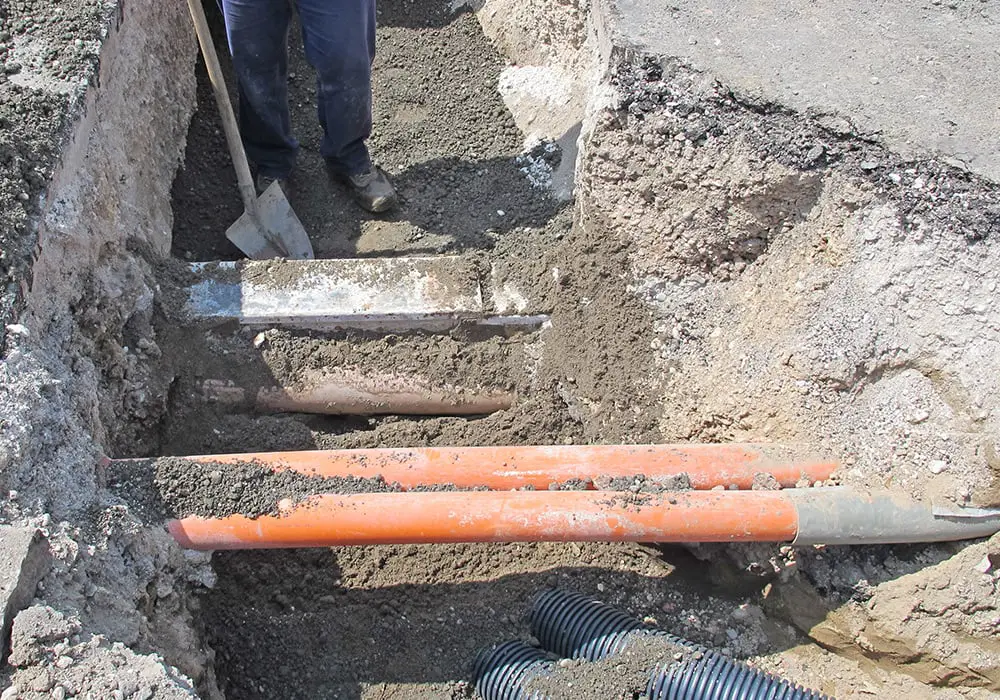

How Deep to Bury Electrical Wires
When planning to bury electrical wires underground, it’s essential to consider the appropriate depth to ensure safety and compliance with regulations. The depth to bury electrical wires varies depending on the type of cable and application.
For direct burial cables like USE/USE-2, UF-B, Copper Tracer, and Aluminum URD, the depth may differ. Typically, a minimum depth of 450 mm (18 inches) is required for buried cable in the UK. However, if you’re installing galvanized rigid metal electrical conduit with individual insulated wires, you should bury them only 150 mm deep (6 inches). The wires must be rated for use in a wet location, such as Type THWN-2 (thermoplastic/wet location/nylon jacket).
When installing cable in a concrete floor, SWA cable or conduit must be protected with at least 25 mm (1 inch) of concrete. Furthermore, cables should be laid on a sand base and covered with a loose road stone mixture before covering with soil. This way, it’s unlikely that any excavation would come into contact with the armoured cable. For supplying power to sheds, you can also run the cable at a shallower depth of 150 mm (6 inches).
To ensure electrical safety, it’s common practice to bury an electrical warning marker tape (similar to crime scene tape) halfway above the electrical wiring in the trench. This serves as a visual warning for anyone who might accidentally dig in the area where the cable is buried.
Remember to consult local regulations and guidelines on the appropriate depth to bury electrical wires in your area. Following best practices and guidelines not only ensures safety but also helps you stay compliant with applicable electrical codes.
Effective Protective Measures
When it comes to burying electrical wires underground, there are several protective measures you should follow to ensure safety and longevity of the cables. By adhering to these guidelines, you can minimise the risk of damage and accidents.
Firstly, the type of electrical wire is crucial. You should opt for a direct-burial rated cable, which is specifically designed for outdoor use and able to withstand various environmental factors. This kind of cable is typically engineered for underground use, even without the need for a conduit.
Next, consider the depth at which the cable will be buried. Direct-burial Type UF cables should be installed at a minimum depth of 12 inches (30.5 cm) and protected by a ground-fault circuit interrupter (GFCI). This GFCI protection ensures enhanced electrical safety while reducing the need for a deeper trench. Other types of cables might require a minimum depth of 18 inches (45.7 cm) to ensure adequate protection.
In addition to burying the cables at the proper depth, it’s essential to provide a strong and suitable conduit, should you choose to use one. Conduits can be made of PVC, galvanised steel, or rigid metal, each having their own merits, but ensure that whichever you choose is specifically designed for underground installations. This will decrease the likelihood of damage from external factors, such as water, rodents, or physical stress.
When working near electrical cables, make sure to take precautions to avoid coming into contact with them. This includes marking the area where cables are buried and adhering to regulations when digging or performing any excavation tasks. Adhering to such precautions can significantly reduce the risk of injury or fatality due to accidental contact with hidden cables.
Moreover, regular inspections, maintenance, and repairs can help you identify and address any potential issues that may arise. By doing so, you can avoid accidents and extend the life of your buried electrical cables.
By following these effective protective measures, you can minimise risks, ensure safe underground electrical installations, and achieve better longevity for your buried cables.
UK Regulatory Standards for Burying Electrical Wires
When burying electrical wires underground in the UK, it is essential to follow the regulatory standards to ensure safety and compliance. There are specific depths and materials required for different types of cables and conduits.
Direct-Buried Type UF Cable: If you choose to bury GFCI-protected direct-buried Type UF (Underground Feeder) cable, the minimum depth required is 12 inches. The protection offered by GFCI devices enhances electrical safety while reducing the need for a deeper trench.
PVC Conduit with Insulated Wires: If you opt for using PVC conduit with individual insulated wires, the required minimum depth is 18 inches. This method offers additional protection against potential damage to the cables.
It’s important that you follow the British Standard BS 7671:2018, frequently referred to as the IET Wiring Regulations. This standard includes guidelines and requirements related to the installation and maintenance of electrical systems, including those for underground electrical cables.
Remember to always consult a professional electrician who is familiar with British regulatory standards before undertaking any electrical projects. They can help ensure that your installation is both safe and compliant with local regulations.